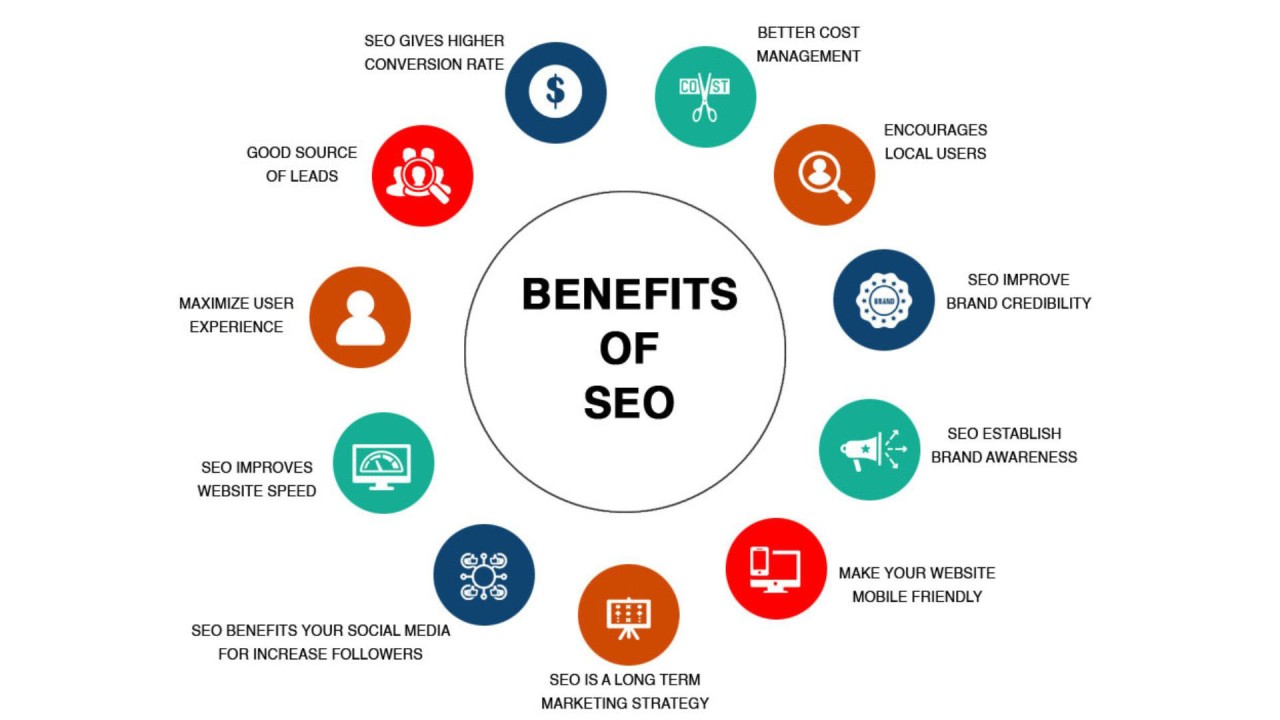
A comprehensive SEO audit is essential for identifying and fixing website issues that could be hindering your search engine performance. Regular audits help ensure your site is optimized for search engines, improving visibility, traffic, and ultimately, conversions. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of performing an SEO audit, covering technical, on-page, and off-page aspects.
Step 1: Crawl Your Website
Start by crawling your website to get an overview of its structure and identify any technical issues. Use tools like Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, or DeepCrawl to perform this task.

Key Areas to Analyze:
Broken Links: Identify and fix broken internal and external links.
Duplicate Content: Locate duplicate content issues that could confuse search engines.
URL Structure: Ensure URLs are clean, descriptive, and follow a logical structure.
Step 2: Analyze Technical SEO
Technical SEO forms the backbone of your website’s search engine performance. Ensuring your site is technically sound is crucial for effective SEO.

Technical SEO Checklist:
Site Speed: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to check your site’s load time. Optimize images, leverage browser caching, and minimize code to improve speed.
Mobile-Friendliness: Verify your site is mobile-friendly using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. Ensure responsive design and usability across all devices.
XML Sitemap: Ensure your XML sitemap is correctly formatted and submitted to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
Robots.txt: Check your robots.txt file to ensure it’s not blocking important pages from being crawled by search engines.
SSL Certificate: Ensure your website uses HTTPS, providing a secure connection for users and a ranking boost from Google.
Step 3: On-Page SEO Analysis
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic.

On-Page SEO Elements:
Title Tags: Ensure each page has a unique, descriptive, and keyword-optimized title tag.
Meta Descriptions: Craft compelling meta descriptions that accurately summarize the page content and include target keywords.
Headers (H1, H2, H3, etc.): Use header tags to structure your content hierarchically and include relevant keywords.
Keyword Optimization: Analyze keyword usage across your pages. Ensure keywords are naturally integrated into content, headers, and meta tags without keyword stuffing.
Content Quality: Assess the quality of your content. Ensure it’s valuable, engaging, and relevant to your target audience. Update any outdated information.
Internal Linking: Check your internal linking structure. Ensure you’re linking to relevant pages to improve navigation and distribute link equity.
Step 4: Off-Page SEO Analysis
Off-page SEO involves activities outside your website that impact rankings, such as backlinks and social signals.

Off-Page SEO Checklist:
Backlink Profile: Use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to analyze your backlink profile. Look for toxic or spammy links that could harm your site and disavow them if necessary.
Competitor Analysis: Examine your competitors’ backlink profiles to identify potential link-building opportunities.
Social Signals: Evaluate your social media presence. Ensure your content is shareable and engages users across platforms.
Step 5: User Experience (UX) Analysis
User experience is a critical factor for both SEO and user satisfaction. A positive UX can reduce bounce rates and increase dwell time.

UX Factors to Consider:
Navigation: Ensure your site is easy to navigate. Use clear menus and logical structure to help users find information quickly.
Design: Your site’s design should be clean, professional, and aligned with your brand. Ensure it’s visually appealing on all devices.
Engagement: Analyze user engagement metrics like bounce rate, average session duration, and pages per session. Identify and address pages with high bounce rates or low engagement.
Step 6: Local SEO (if applicable)
If you have a local business, optimizing for local search is crucial.
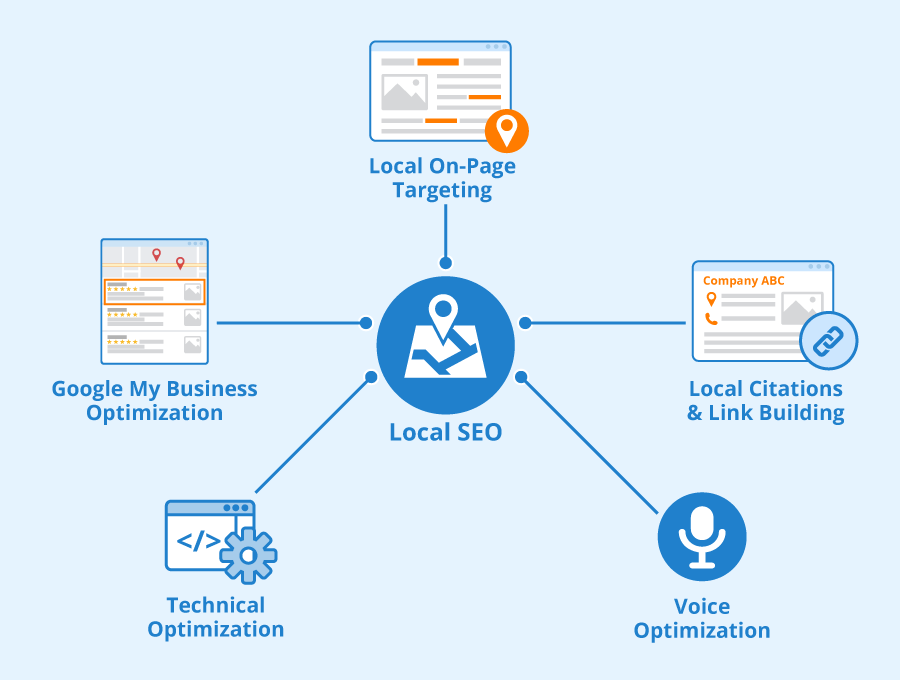
Local SEO Checklist:
Google My Business: Ensure your Google My Business listing is complete and optimized with accurate information, including address, phone number, and business hours.
NAP Consistency: Check the consistency of your Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP) across all online directories and your website.
Local Keywords: Optimize your content with local keywords relevant to your business and location.
Reviews: Encourage satisfied customers to leave positive reviews on your Google My Business listing and other review platforms.
Step 7: Reporting and Action Plan
Once you’ve completed the audit, compile your findings into a comprehensive report. Highlight the issues identified and provide actionable recommendations to address them.

Creating the Action Plan:
Prioritize Issues: Rank issues based on their impact on SEO and user experience. Address critical issues first.
Assign Tasks: Delegate tasks to relevant team members or departments. Set deadlines for completion.
Monitor Progress: Regularly review the progress of implemented changes and their impact on SEO performance.
Conclusion
Conducting a comprehensive SEO audit is an essential practice for maintaining and improving your website’s search engine performance. By following this step-by-step guide, you can identify and fix critical issues, enhance user experience, and boost your SEO efforts. Regular audits will help you stay ahead of the competition and ensure your website remains optimized for both search engines and users.